DACUM: Bringing New Apprenticeships to Life
Apprenticeship is an age-old, time-tested approach to educating and building a skilled workforce while simultaneously filling workforce needs. Apprentices enter the workforce immediately, pairing job education and experience with more traditional classroom learning experiences. New apprentices are emerging in non-traditional apprenticeship fields, requiring thorough and rapid development to help fill a growing skills gap.
WIDS used the DACUM model to support development of several new Wisconsin Apprenticeships under the American Apprenticeship Initiative. The Wisconsin Bureau of Apprenticeship Standards (WI-BAS) and the Wisconsin Technical College System contracted with WIDS to facilitate the development of non-traditional apprenticeships in IT, Healthcare, and Advanced Manufacturing.
What do IT Service Desk Professionals Do?
The first question to answer when developing a new apprenticeship is, “What tasks does a skilled worker perform on the job?” In the development of the IT-Service Desk (Help Desk) apprenticeship, six industry  experts, including front-line service desk experts and supervisors, joined forces to define the work all IT Service Desk professionals must perform. The DACUM (Developing A CurriculUM) process was used to perform the occupational analysis. DACUM relies on the experiences of workers and employers, drawing on their expertise to identify current job duties and tasks. Duties and tasks lead to learner outcomes or competencies.
experts, including front-line service desk experts and supervisors, joined forces to define the work all IT Service Desk professionals must perform. The DACUM (Developing A CurriculUM) process was used to perform the occupational analysis. DACUM relies on the experiences of workers and employers, drawing on their expertise to identify current job duties and tasks. Duties and tasks lead to learner outcomes or competencies.
A WIDS consultant led the DACUM process, collecting a list of duties from the participants using a structured brainstorming format. Common themes were grouped, and the scope of the apprenticeship narrowed quickly as duties and tasks were documented visually. Open inquiry and conversation soon uncovered the path to a profession focused on problem solving, case management and client care skills.
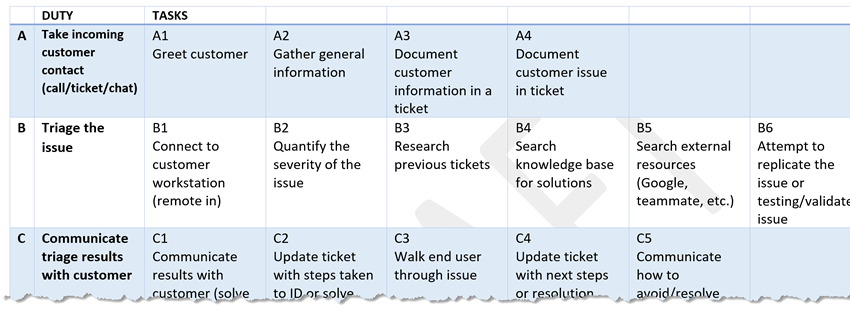
Fig. 1: DACUM Chart illustrating duties and tasks of the IT Service Desk professional
While the bulk of a DACUM focuses on duties and tasks, underlying knowledge, attitudes, and trends are captured to complete the DACUM. The industry experts brainstormed these ideas and were added to the DACUM chart.
To validate the DACUM, a survey was developed and distributed to a larger audience of IT Service Desk professionals. The survey results provided insight to the Service Desk tasks. WIDS compiled the survey results, validating the content identified by the DACUM team. Results helped the team identify priorities, based on the tasks with the highest degree of frequency, criticality, and difficulty.
Where are Skills Learned?
Once the DACUM is validated, the occupation is clearly defined. The apprenticeship team knows WHAT the worker should do.
The next step is identifying where the apprentice will learn each task. Apprenticeship involves about 80% on the job learning (OJL) and 20% classroom related instruction (RI). The team created a simple chart showing the distribution of OJL and RI among the DACUM tasks. The team also noted apprentices learn some tasks in both settings.
Fig. 2: IT Service Desk DACUM Tasks assigned location of learning: On the Job, Related Instruction, or Both
Job Books and Courses
Wisconsin creates Job Books to detail the on the job learning and Course Outcome Summaries to define the related instruction.
WIDS led development of the related instruction, along with some DACUM team members and technical college instructors. The DACUM tasks identified for related instruction were organized into logical groups. The WIDS Instructional Design Model gave the team a framework for linking DACUM duties to the related instruction program outcomes. DACUM tasks were linked to course competencies or student learning outcomes. The knowledge, attitudes, and trends collected in the DACUM provided a source for performance standards and learning objectives. The team’s work resulted in three related instruction courses under one apprenticeship program. All the information was documented in WIDS software: program outcomes, course competencies, learning objectives and performance standards.
WIDS software became the home base for the new IT Service Desk Apprenticeship Program. The software provided the team an easy way to generate a variety of curriculum maps, ensuring the validated DACUM results are addressed in the appropriate related instruction coursework.
WIDS lets the team see at a glance how the three courses relate to external standards (DACUM duties and tasks).
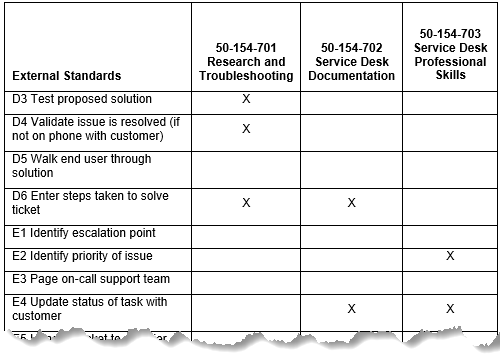
Fig. 4: DACUM Tasks (External Standards) mapped to apprenticeship related instruction courses
WIDS also gives the team a Course Outcome Summary report, pulling together the work complete at each stage of the DACUM.
Fig. 5: DACUM results integrated into course outcomes as program outcomes (Duties) and Target Standards (Tasks)
With a validated IT Service Desk apprenticeship, program graduates can whet their curiosity about multiple IT professions, potentially fueling a passion for further career advancement.
DACUM is an important process that focuses occupational tasks and prevent scope creep. In this case, the WIDS-led DACUM resulted in one of Wisconsin’s first IT-focused apprenticeships.
Interested in WIDS helping you create a new program using DACUM? Contact us!
Download the Sample DACUM Chart
8706